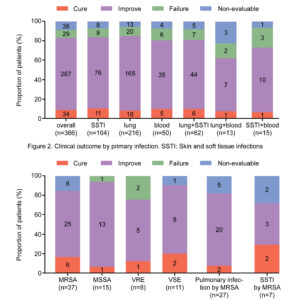
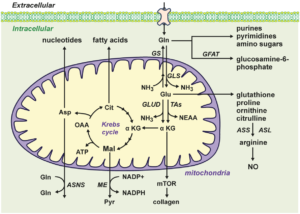
Immunological effects of glutamine supplementation in polytrauma patients in intensive care unit
Ref: Cotoia et al. J Anesth Analg Crit Care (2022) 2:41, https://doi.org/10.1186/s44158-022-00068-1 Glutamine (GLN) is classified as a non-essential amino acid and it is released from skeletal muscle to be a constituent of proteins . Furthermore, GLN acts as an immune stimulator as an essential component for lymphocyte proliferation and cytokine production,