Introduction:
Coronary artery disease (CAD) continues to be a leading cause of death and arterial hypertension is one of the major risk factor for CAD development and progression. Non-invasive diagnosis of coronary artery disease in hypertension, however, remains a major clinical challenge2 Early and effective identification and treatment of CAD in hypertensive patients are recommended. In this paper, we highlight the potential additional value of an accurate CV risk stratification, with the aim to effectively implement the clinical decision-making process that leads to the current diagnostic use of CA. An accurate CV risk stratification applied to the choice of diagnostic test for CAD screening may help clinicians to overcome the hurdles of this diagnosis, so that the costs of ineffective testing could be substantially minimized. In addition, diagnosis of CAD in hypertension could help to define targets of treatment, reducing the risk related to an excessive blood pressure lowering2
Diagnostic Methods and Techniques for CAD Detection in Hypertension2
1. Non-Invasive Screening Tests – The available tests currently proposed to detect CAD in hypertensive population2
2. Invasive Screening Tests – Selective coronary angiography3
CA still represents the “gold standard” to diagnose CAD in clinical practice. More than 2.5 million CA are performed every year in Europe and in the United States3
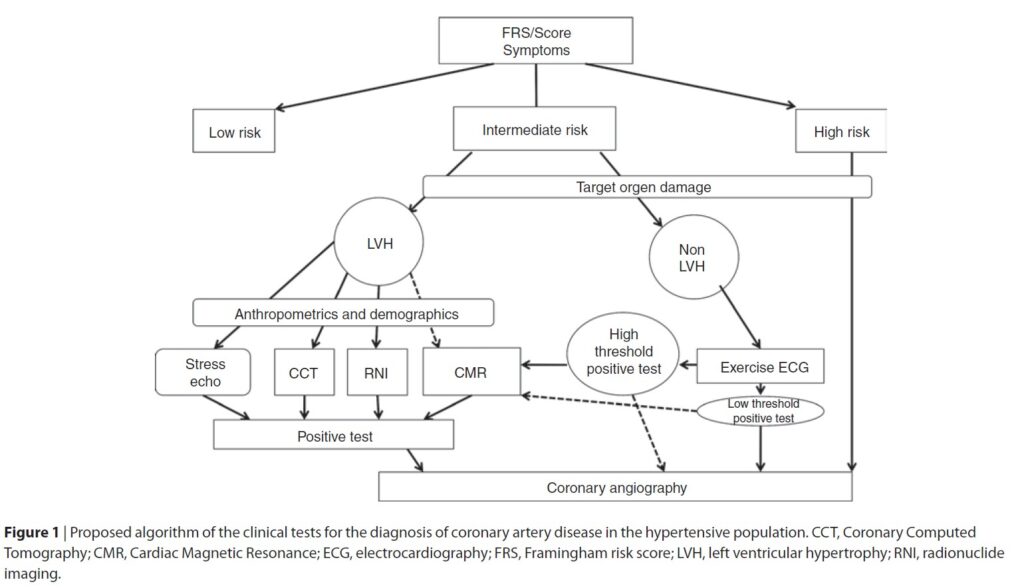
Developing Algorithms for Improving CAD Diagnosis in Hypertension2:
The use of any single diagnostic tool is often inadequate for the accurate detection of CAD in hypertensive patients. Moreover, routine performance of CA in unselected hypertensive patients should not be recommended as a first choice, not only because the test is invasive, but also because of the low diagnostic yield2